-
drpvashistha@gmail.com
- +91 9004229819
Cholangiopancreatography in Mumbai, Navi Mumbai
Cholangiopancreatography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts. It involves injecting a contrast dye into these ducts, followed by X-ray or other imaging modalities to create detailed images of the biliary and pancreatic systems. This procedure helps diagnose and evaluate conditions such as gallstones, tumors, or blockages in these ducts.
Cholangiopancreatography In Mumbai and Navi Mumbai at Dr. Purushottam Vashistha Clinic is a diagnostic procedure widely used to visualize the bile ducts and pancreas. This medical imaging technique involves injecting a contrast dye into the ducts and then using X-rays to create detailed images of these structures.
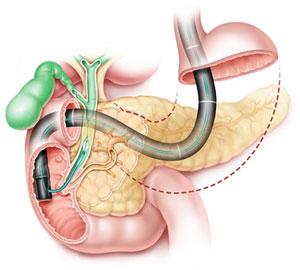
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) is a common variant of this procedure, where an endoscope is passed through the mouth and into the duodenum to access the ampulla of Vater. From there, a catheter is inserted to inject the contrast dye directly into the bile and pancreatic ducts, allowing for precise visualization and identification of any abnormalities such as stones, strictures, or tumors.
Procedure of Cholangiopancreatography
Dr. Purushottam Vashistha is a renowned specialist in gastroenterology, ensuring precise and expert care for patients undergoing this diagnostic procedure. The process involves injecting contrast material into the ducts followed by imaging, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various hepatobiliary and pancreatic conditions. Below is the procedure of Cholangiopancreatography:
- Patient Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient is typically asked to fast for a certain period to ensure the gallbladder is filled with bile. Intravenous (IV) access is established, and the patient may be given medications to relax or induce mild sedation.
- Insertion of Endoscope: Cholangiopancreatography involves the use of an endoscope, a flexible tube with a light and camera at its tip. The endoscope is inserted through the mouth, down the esophagus, and into the stomach and duodenum.
- Locating the Ampulla of Vater: The endoscope is maneuvered to locate the ampulla of Vater, which is the opening where the bile and pancreatic ducts drain into the duodenum. Once located, a catheter is inserted through the endoscope to access this opening.
- Contrast Agent Injection: A contrast agent, a dye visible on X-rays, is injected into the bile and pancreatic ducts through the catheter. This helps outline the ducts and allows for the visualization of any abnormalities or blockages.
- X-ray Imaging: X-ray images are taken as the contrast agent flows through the ducts. This provides real-time imaging of the biliary and pancreatic systems, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions such as gallstones, strictures, or tumors.
- Conclusion and Potential Interventions: After imaging is complete, the endoscope is withdrawn, and the patient is observed. Depending on the findings, further interventions may be planned, such as removing gallstones, placing stents to alleviate blockages, or taking tissue samples for biopsy.
Why Cholangiopancreatography is done?
Cholangiopancreatography is performed to visualize and diagnose issues in the bile ducts and pancreas. This medical imaging technique, commonly done through endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), helps identify conditions like gallstones, inflammation, tumors, or strictures within the biliary and pancreatic systems.
It is crucial for assessing conditions such as cholangitis, pancreatitis, or obstructive jaundice. Additionally, cholangiopancreatography aids in planning appropriate interventions, such as the removal of gallstones or placement of stents, contributing to effective management and treatment strategies for patients with hepato-pancreatico-biliary disorders.